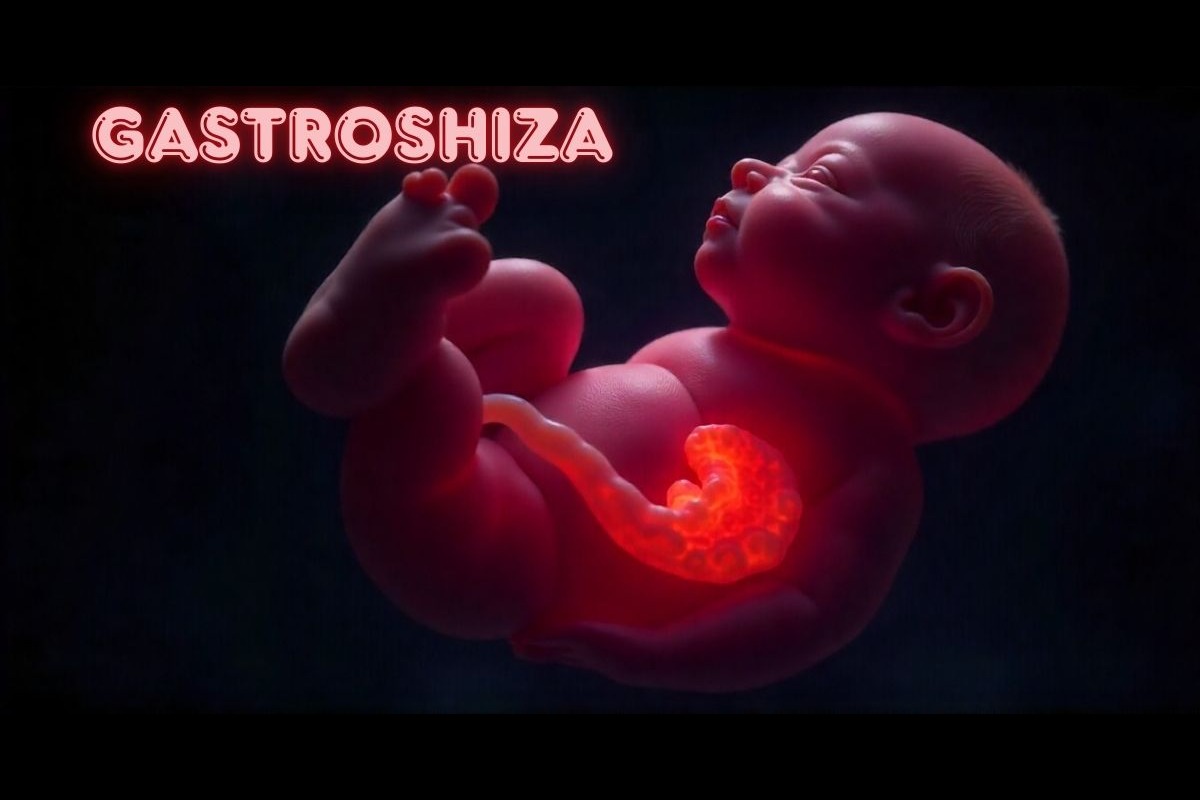
What is gastroshiza?
Gastroshiza is a rare congenital disorder characterized by abnormal development of the abdominal wall, resulting in protrusion of the intestines and sometimes other organs. Unlike other similar conditions, a gastroshiza hernia typically develops through an opening near the navel and is not covered by a protective membrane. This unique presentation requires specific medical attention and immediate intervention after birth.
Causes and Risk Factors of Gastroshiza
Genetic and Environmental Influences
The exact causes of gastroshiza are still under investigation, but a genetic predisposition and environmental factors may contribute. Possible risk factors include:
Young mothers (especially those under 20)
Exposure to toxins such as tobacco, alcohol, or certain medications during pregnancy
Mothers with poor prenatal nutrition
Although most cases appear to occur sporadically with no clear hereditary origin, studies are ongoing to search for an underlying genetic link.
Differences Between Gastroshiza and Similar Conditions
Gastroshiza and omphalocele are often confused. The main distinction lies in the absence of a protective membrane around the organs in gastrosis, while omphalocele involves a herniation within a membrane. This difference influences not only the surgical approach but also the prognosis and potential complications.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Gastrosis is almost always visible immediately after birth. Its most characteristic symptom is the protrusion of abdominal organs through an opening located near, but not directly above, the navel. These exposed organs, usually loops of intestine, are particularly vulnerable to injury, dehydration, and infection.
Diagnostic Procedures
Prenatal ultrasound: Most cases are currently detected during a routine prenatal examination in the second trimester.
Physical examination: Confirmation is made at birth through a visual examination by medical personnel.
Additional tests may be necessary to assess the extent of the hernia and the condition of the exposed organs
Complications Associated with Gastroshiza
Early diagnosis is crucial, as exposed intestines are prone to complications such as:
Dehydration (loss of body fluids)
Infection (absence of protective membrane)
Intestinal dysfunction, which can lead to malabsorption or short bowel syndrome
Some babies may have other congenital malformations, but these are less common in cases of gastrositis than in cases of omphalocele.
Treatment Options for Gastroshiza
Immediate Postnatal Care
After delivery, the medical team acts quickly to protect exposed organs:
By covering them with sterile, moist dressings
By using special plastic covers (silos) to minimize the risk of infection
By preventing heat and fluid loss
Surgical Intervention
The definitive treatment for gastrositis is surgical repair. Depending on the severity, this can be performed in two main ways:
Primary repair: If the opening and inflammation are small, the organs are reimplanted into the abdomen in a single procedure.
Staged repair: For larger lesions, the organs are gradually repositioned over several days using a silo before final closure.
Supportive medical care, including nutritional and respiratory support, is essential throughout the healing process.
Prognosis and long-term outcomes
The prognosis for babies born with gastrositis has improved considerably thanks to modern medical techniques. Most babies recover well after surgery and lead healthy lives, although some may suffer from long-term digestive problems. Continuous follow-up is necessary to monitor development, nutrition, and potential complications.
Preventive Measures and Maternal Health
Although gastrositis cannot always be avoided, pregnant women can reduce their risk by adopting the following measures:
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and receiving appropriate prenatal care
Avoiding tobacco, alcohol, and non-prescription medications
Receiving regular prenatal checkups
Early detection through prenatal care improves outcomes and allows families to prepare for necessary interventions after delivery.
Support and Resources for Families
A diagnosis of gastrosemia can be overwhelming, but families benefit from multidisciplinary care teams, including surgeons, neonatologists, nurses, and nutritionists. Peer support and counseling services are also available to help families overcome challenges and celebrate successes after successful treatment.